Laparoscopic Biliopancreatic Diversion (Scopinaro procedure) (BPD) India offers information on Laparoscopic Biliopancreatic Diversion (Scopinaro procedure) (BPD) in India, Laparoscopic Biliopancreatic Diversion (Scopinaro procedure) (BPD) cost India, Laparoscopic Biliopancreatic Diversion (Scopinaro procedure) (BPD) hospital in India, Delhi, Mumbai, Chennai, Hyderabad & Bangalore, Laparoscopic Biliopancreatic Diversion (Scopinaro procedure) (BPD) Surgeon in India
A biliopancreatic diversion changes the normal process of digestion by making the stomach smaller and allowing food to bypass part of the small intestine so that you absorb fewer calories.
You will feel full more quickly than when your stomach was its original size, which reduces the amount of food you eat and thus the calories consumed. Bypassing part of the intestine also means that you will absorb fewer calories. This leads to weight loss.
Procedure
There are two biliopancreatic diversion surgeries: a biliopancreatic diversion and a biliopancreatic diversion with duodenal switch.
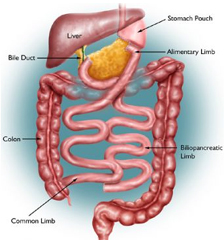
In a biliopancreatic diversion, a portion of the stomach is removed. The remaining portion of the stomach is connected to the lower portion of the small intestine.
In a biliopancreatic diversion with duodenal switch, a smaller portion of the stomach is removed, but the remaining stomach remains attached to the duodenum (the upper part of the small intestine). The duodenum is connected to the lower part of the small intestine.
These procedures can be done by making a large incision in the abdomen (an open procedure) or by making a small incision and using small instruments and a camera to guide the surgery (laparoscopic approach).
 What To Expect After Surgery
What To Expect After Surgery
Surgery for obesity usually involves a 4- to 6-day hospital stay (2 to 3 days for a laparoscopic approach). Most people can return to their normal activities within 3 to 5 weeks.
A biliopancreatic diversion may cause dumping syndrome. This occurs when food moves too quickly through the stomach and intestines. It causes nausea, weakness, sweating, faintness, and possibly diarrhea soon after eating. These symptoms are made worse by eating highly refined, high-calorie foods (like sweets). In some cases you may become so weak that you have to lie down until the symptoms pass. Dumping syndrome does not occur in a biliopancreatic diversion with duodenal switch.
Risks
Risks common to all surgeries for weight loss include an infection in the incision, a leak from the stomach into the abdominal cavity or where the intestine is connected (resulting in an infection called peritonitis), and a blood clot in the lung (pulmonary embolism). About one-third of all people having surgery for obesity develop problems related to poor nutrition, such as anemia or osteoporosis.2, 3
Fewer than 3 in 200 (1.5%) people die after surgery for weight loss.2
Biliopancreatic diversion surgeries result in reduced absorption of protein, fat, calcium, iron, and vitamins B12, A, D, E, and K. You may have frequent, bad-smelling stools and a higher risk for developing osteoporosis.
Within 1 year of biliopancreatic diversion surgery:1
30 out of 100 people develop anemia.
30 to 50 people out of 100 develop a deficiency in vitamins A, D, E, K, and beta-carotene.
About 4 people out of 100 need hospitalization because of lack of protein. Protein deficiency is somewhat less of a risk in the biliopancreatic diversion with duodenal switch.
Advantages
Greater stomach capacity (200-250 mls) therefore can eat a small main meal instead of an entrée portion.
Best weight loss of all techniques 70-90% EWL over 2yrs
Weight loss is well maintained
Adjustable and partially reversible, but only by further surgery.
A very good option for revision if other techniques have failed.
Disadvantages
Open operation ( usually), therefore greater operative risks e.g infection, Bowel leak, Clots to legs and lungs wound infection and hernia, chest infection. Risk of Death 1:200
Malabsorbtion to some minerals vitamins and Protein . Patients must commit to taking lifelong supplements of the fat soluble vitamins ( A D E K ) Calcium and sometimes Iron.
Risk of deficiency state e.g. Iron deficiency anaemia or osteoporosis if supplements not taken
Take longer to recover ( 6-8 weeks off work)
Requires removal of Gall bladder because of high incidence of stone formation
Increased stool frequency 2-4/day
Flatulance if fatty foods eaten