Orthopedic Surgery



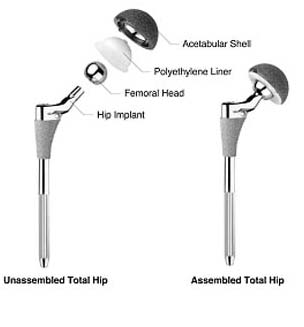 The surgeon begins by making an incision on the side of the thigh to allow access to the hip joint. Once the hip joint is entered, the surgeon dislocates the femoral head from the acetabulum. Then the femoral head is removed by cutting through the femoral neck with a power saw.
The surgeon begins by making an incision on the side of the thigh to allow access to the hip joint. Once the hip joint is entered, the surgeon dislocates the femoral head from the acetabulum. Then the femoral head is removed by cutting through the femoral neck with a power saw. 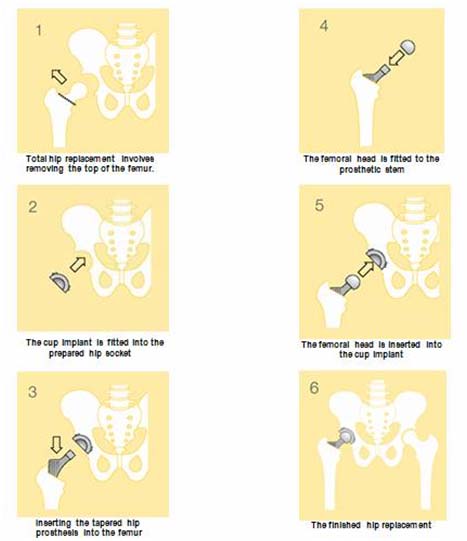
India Surgery Computer Hip Replacement, Cost Hip Computer Navigation, Computer Navigation Hip Replacement, Computer Navigation Hip Replacement Surgery, Hip Replacement Surgery, Computer, Navigation, Hip, Total Hip Replacement, Computer Assisted Navigational Surgery, Joint Replacement, Hip Replacement Specialist, Healthcare, Patient, Computer Navigation Assisted Hip Replacement, India Acetabular Component Position, Computer Navigation, Utilizing Computer Navigation, India Surgery Tour, Role Of Computer-Assisted Navigation, Hip Replacement, Information