Brain Tumors India offers information on Brain Tumors in India, Brain Tumors cost India, Brain Tumors hospital in India, Delhi, Mumbai, Chennai, Hyderabad & Bangalore, Brain Tumors Surgeon in India
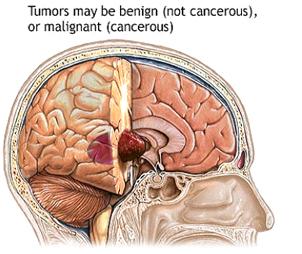 Fig :
Fig : Brain Tumors
A tumor is any mass caused by abnormal or uncontrolled growth of cells. Tumors in the brain are categorized according to several factors, including where they're located, the type of cells involved, and how quickly they're growing.
They can be benign (noncancerous, meaning that they do not spread elsewhere or invade surrounding tissue) or malignant (cancerous).
Cancerous brain tumors are further classified as either primary or secondary tumors. Primary tumors start in the brain, whereas secondary tumors spread to the brain from another site such as the breast or lung.
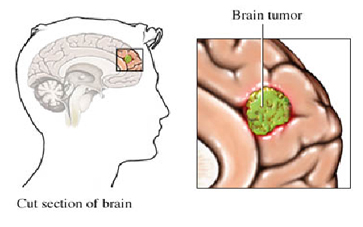 Fig :
Fig : Brain Tumors
Benign Tumor
The term "benign" refers to a condition, tumor, or growth that is not cancerous. This means that it does not spread to other parts of the body or destroy nearby tissue. Benign tumors usually grow slowly. If a benign tumor is big enough, its size and weight can press on nearby blood vessels, nerves, or organs, or otherwise cause problems. While some benign brain tumors may pose a health risk, including risk of disability and death, most are usually successfully treated with techniques such as surgery.
Types Of Brain Tumor
- Acoustic neurinoma : Benign tumor occurring in the 8th cranial nerve (the acoustic nerve) between the pons and the cerebellum. Possibly associated with neurofibromatosis. The term "acoustic neuroma" is actually a misnomer since it this a primary intracranial tumor of the myelin forming cells called "Schwann cells" (schwannoma).
- Astrocytomas : This represent the most common type of glioma. They develop from the supporting cells of the brain, which are star-shaped glial cells called astrocytes.
- Oligodendroglioma : These are tumours that are made up of cells known as oligodendrocytes, which produce the fatty covering of nerve cells: the myelin sheath. They are usually slower-growing than astrocytic tumours.
- Ependymoma : Tumor arising from the ependymal cells found along the ventricles and central canal of the spinal cord.
- Brain stem glioma : The tumor occurs in the lowest part of the brain. Brain stem gliomas most often are diagnosed in young children and middle-aged adults
- Craniopharyngioma : This is a benign, congenital tumor. It is cystic and occurs primarily in children and adolescents. Craniopharyngiomas occur in the sellar region. They often involve the third ventricle, optic nerve, and pituitary gland. These are localized tumors that grow by expansion. Malignancy and metastasis are unknown.
- Medulloblastoma : This tumor usually arises in the cerebellum. It is the most common brain tumor in children. It is sometimes called a primitive neuroectodermal tumor
- Meningioma : Benign tumor arising from the meninges, the membranes covering the brain and spinal cord. Meningiomas represent approximately 20% of all primary brain tumors and occur most commonly in middle-aged women.
- Germ cell tumor of the brain : The tumor arises from a germ cell. Most germ cell tumors that arise in the brain occur in people younger than 30. The most common type of germ cell tumor of the brain is a germinoma.
- The pineal gland is just below the area where the two cerebral hemispheres join. Tumours in this part of the brain are extremely rare. They can be made up of different types of cells. The most common tumors are germinomas; others include teratomas, pineocytomas and pineoblastomas.
Primary Malignant Tumor
Tumors that begin in brain tissue are known as primary brain tumors. Although primary brain tumors often shed cancerous cells to other sites in the central nervous system (the brain or spine), they rarely spread to other parts of the body.
Secondary Malignant Tumor
When cancer cells spread to the brain from another organ (such as the lung or breast), is called as a secondary tumor or metastatic tumor. Secondary tumors in the brain are far more common than primary brain tumors.
Causes Of Brain Tumors
The cause of primary brain tumors is unknown. This is because they are rare, there are many types, and there are many possible risk factors that could play a role. Exposure to some types of radiation, head injuries, and hormone replacement therapy may be risk factors, as well as many others. The risk of using cell phones is hotly debated.
Some inherited conditions increase the risk of brain tumors, including neurofibromatosis, Von Hippel-Lindau syndrome, Li-Fraumeni syndrome, and Turcot's syndrome.
Tumors may occur at any age, but many specific tumors have a particular age group in which they are most common. In adults, gliomas and meningiomas are most common.
Exposure to vinyl chloride is an environmental risk factor for brain cancer. Vinyl chloride is a carcinogen, that is, a cancer-causing substance. It is used in manufacturing plastic products such as pipes, wire coatings, furniture, car parts, and housewares, and is present in tobacco smoke.
Symptoms Of Brain Tumor
The most common symptoms include headaches, which can be most severe in the morning; nausea or vomiting, which can be most severe in the morning; seizures or convulsions; difficulty thinking, speaking, or finding words; personality changes; weakness or loss of feeling in the arms or legs; loss of balance; abnormal eye movements or change in vision; confusion and disorientation; change in personality or memory. Different parts of the brain control different functions, so symptoms will vary depending on the tumor's location.
Diagnosis Of Brain Tumors
A brain tumor diagnosis usually involves several steps, which can include a neurological examination, brain scan(s) and/or a biopsy. A neurological examination is a series of tests to measure the function of the patientís nervous system and physical and mental alertness. The doctor also examines the eyes to look for swelling caused by a tumor pressing on the nerve that connects the eye and brain.
MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) is a scanning device that uses magnetic fields and computers to capture images of the brain on film. The MRI detects signals emitted from normal and abnormal tissue, providing clear images of most tumors.
CT Scan (Computed Tomography) combines sophisticated x-ray and computer technology. CT can show a combination of soft tissue, bone, and blood vessels. CT images can determine some types of tumors, as well as help detect swelling, bleeding, and bone and tissue calcification.
PET SCAN : The PET scan measures the brains activity and sends this information to a computer, which creates a live image. Doctors use PET scans to see the difference between scar tissue, recurring tumor cells, and necrosis (cells destroyed by radiation treatment).
Biopsy : The removal of tissue to look for tumor cells is called a biopsy. A pathologist looks at the cells under a microscope to check for abnormal cells. A biopsy can show cancer, tissue changes that may lead to cancer, and other conditions. A biopsy is the only sure way to diagnose a brain tumor.
Treatment
The common treatments for Neurosurgery are as follows :
 Tumor Surgery
Tumor Surgery
 Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy
 Radiotherapy
Radiotherapy